Dynamic Programming 动态规划
Dynamic Programming 动态规划
This blog records the solutions I made for the Dynamic Programming questions from Leetcode.
Fibonacci related problems
Firstly, find out the transformation function for the problem.
Then, from the starting point to calculate the results by iterating the array.
Finally, reach and output the final result.
Typically, we don't have to persist all the intermediate results and only three or four states is needed.
T70. Climbing Stairs
You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Example 1:
Input: n = 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: n = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 45
My Solution
We find that the ways we used to reach n only depends on the ways to n-1 and n-2. So we can conclude that f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2). We use p to represent n-2 steps and q for n-1 steps. So we can get:
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
int p = 0, q = 1;
int next;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
next = p + q;
p = q;
q = next;
}
return next;
}
};
T509. Fibonacci Number
The Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted F(n) form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2), for n > 1.
Given n, calculate F(n).
Example 1:
Input: n = 2
Output: 1
Explanation: F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1.
Example 2:
Input: n = 3
Output: 2
Explanation: F(3) = F(2) + F(1) = 1 + 1 = 2.
Example 3:
Input: n = 4
Output: 3
Explanation: F(4) = F(3) + F(2) = 2 + 1 = 3.
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 30
My Solution
The same logic as the above question.
class Solution {
public:
int fib(int n) {
int p = 0; int q = 1;
if (n == 0) {return p;}
if (n == 1) {return q;}
int next;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++ ){
next = p + q;
p = q;
q = next;
}
return next;
}
};
1137. N-th Tribonacci Number
The Tribonacci sequence Tn is defined as follows:
, , , and for n >= 0.
Given n, return the value of .
Example 1:
Input: n = 4
Output: 4
Explanation:
T_3 = 0 + 1 + 1 = 2
T_4 = 1 + 1 + 2 = 4
Example 2:
Input: n = 25
Output: 1389537
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 37- The answer is guaranteed to fit within a 32-bit integer, ie.
answer <= 2^31 - 1.
My Solution
The same logic as the first question.
class Solution {
public:
int tribonacci(int n) {
if (n < 2) {
return n;
}
if (n == 2) {
return 1;
}
int p = 0, q = 1, r = 1;
int next;
for (int i=2; i<n; i++){
next = p + q + r;
p = q;
q = r;
r = next;
}
return next;
}
};
T746. Min Cost Climbing Stairs
You are given an integer array cost where cost[i] is the cost of step on a staircase. Once you pay the cost, you can either climb one or two steps.
You can either start from the step with index 0, or the step with index 1.
Return the minimum cost to reach the top of the floor.
Example 1:
Input: cost = [10,15,20]
Output: 15
Explanation: You will start at index 1.
- Pay 15 and climb two steps to reach the top.
The total cost is 15.
Example 2:
Input: cost = [1,100,1,1,1,100,1,1,100,1]
Output: 6
Explanation: You will start at index 0.
- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 2.
- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 4.
- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 6.
- Pay 1 and climb one step to reach index 7.
- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 9.
- Pay 1 and climb one step to reach the top.
The total cost is 6.
Constraints:
2 <= cost.length <= 10000 <= cost[i] <= 999
My Solution
f(n) = min(f(n-1), f(n-2)) + cost[n]
class Solution {
public:
int min (int p, int q){
return p <= q ? p : q;
}
int minCostClimbingStairs(vector<int>& cost) {
int p =0, q = cost[0];
int len = cost.size();
int nextCost;
for (int i=1; i<len; i++){
nextCost = min(p, q) + cost[i];
p = q;
q = nextCost;
}
return min(p, q);
}
};
T198. House Robber
You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constraint stopping you from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security systems connected and it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses were broken into on the same night.
Given an integer array nums representing the amount of money of each house, return the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without alerting the police.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 1) and then rob house 3 (money = 3).
Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,7,9,3,1]
Output: 12
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 2), rob house 3 (money = 9) and rob house 5 (money = 1).
Total amount you can rob = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 400
My Solution
The robber must rob the house that either is separated by one, or separated by two
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 1){
return nums[0];
}
if (nums.length == 2){
return nums[0] > nums[1] ? nums[0] : nums[1];
}
int p = 0;
int q = nums[0];
int r = nums[1];
int next;
for (int i=2; i<nums.length; i++){
next = nums[i] + (p > q ? p : q);
p = q;
q = r;
r = next;
}
return r > q ? r : q;
}
}
T740. Delete and Earn
You are given an integer array nums. You want to maximize the number of points you get by performing the following operation any number of times:
- Pick any
nums[i]and delete it to earnnums[i]points. Afterwards, you must delete every element equal tonums[i] - 1and every element equal tonums[i] + 1.
Return the maximum number of points you can earn by applying the above operation some number of times.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,4,2]
Output: 6
Explanation: You can perform the following operations:
- Delete 4 to earn 4 points. Consequently, 3 is also deleted. nums = [2].
- Delete 2 to earn 2 points. nums = [].
You earn a total of 6 points.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,2,3,3,3,4]
Output: 9
Explanation: You can perform the following operations:
- Delete a 3 to earn 3 points. All 2's and 4's are also deleted. nums = [3,3].
- Delete a 3 again to earn 3 points. nums = [3].
- Delete a 3 once more to earn 3 points. nums = [].
You earn a total of 9 points.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 1041 <= nums[i] <= 104
My Solution
Firstly, we need to sort the nums
Then, we can conclude that
class Solution {
public int deleteAndEarn(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int idx = 0;
int length = nums.length;
int lastNum = nums[0];
int curNum = nums[0];
int p=0;
int q=0;
int r=0;
for (;idx<length;idx++){
if (nums[idx] == curNum){
r+=nums[idx];
}else{
lastNum = nums[idx-1];
curNum = nums[idx];
break;
}
}
if (idx == length){
return r;
}
int temp;
int next;
while(idx<length){
temp = 0;
for (;idx<length;idx++){
if (nums[idx] == curNum){
temp += nums[idx];
}else {
break;
}
}
if (lastNum == curNum - 1){
next = temp + (p > q ? p : q);
p = q;
q = r;
r = next;
} else {
next = temp + (q > r ? q : r);
p = q;
q = r;
r = next;
}
lastNum = curNum;
if (idx < length){
curNum = nums[idx];
}
}
return r > q? r : q;
}
}
Matrix related problems
T62. Unique Paths
There is a robot on an m x n grid. The robot is initially located at the top-left corner (i.e., grid[0][0]). The robot tries to move to the bottom-right corner (i.e., grid[m - 1][n - 1]). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Given the two integers m and n, return the number of possible unique paths that the robot can take to reach the bottom-right corner.
The test cases are generated so that the answer will be less than or equal to .
Example1:
Input: m = 3, n = 7
Output: 28
Example 2:
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation: From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right
3. Down -> Right -> Down
My Solution
The elements from firstly line and the first column are always 1 because there is only one path.
The state transformation function is .
The following solution records all the intermediate results, but the memory can still be optimised since only the upper row and left column are necessary for the calculation.
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
if (m==1 || n==1){
return 1;
}
int[][] results = new int[m][n];
results[0][0] = 0;
for (int y=0; y<m; y++){
results[y][0] = 1;
}
for (int x=0; x<n; x++){
results[0][x] = 1;
}
for (int y=1; y<m; y++){
for (int x=1; x<n; x++){
results[y][x] = results[y-1][x] + results[y][x-1];
}
}
return results[m-1][n-1];
}
}
T64. Minimum Path Sum
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example 1:
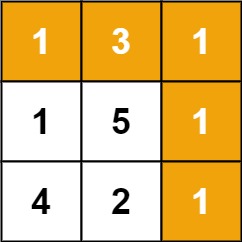
Input: grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1 → 3 → 1 → 1 → 1 minimizes the sum.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
Output: 12
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= grid[i][j] <= 200
My Solution
The same logic as the question above, but with a little changes in initialization and state transformation function.
class Solution {
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length; // columns
int n = grid[0].length; // lines
int[][] results = new int[m][n];
//Init the starting point
results[0][0] = grid[0][0];
//Init the results with the first line and the first column
for (int i=1; i<m; i++){
results[i][0] = grid[i][0] + results[i-1][0];
}
for (int j=1; j<n; j++){
results[0][j] = grid[0][j] + results[0][j-1];
}
// State transformation funciton:
// results[y][x] = min (results[y-1][x], results[y][x-1]) + grid[y][x]
for (int y =1; y<m; y++){
for(int x=1; x<n; x++){
results[y][x] = Math.min(results[y-1][x], results[y][x-1]) + grid[y][x];
}
}
return results[m-1][n-1];
}
}
T63. Unique Paths II
You are given an m x n integer array grid. There is a robot initially located at the top-left corner (i.e., grid[0][0]). The robot tries to move to the bottom-right corner (i.e., grid[m - 1][n - 1]). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time.
An obstacle and space are marked as 1 or 0 respectively in grid. A path that the robot takes cannot include any square that is an obstacle.
Return the number of possible unique paths that the robot can take to reach the bottom-right corner.
The testcases are generated so that the answer will be less than or equal to .
Example 1:

Input: obstacleGrid = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 2
Explanation: There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
Example 2:

Input: obstacleGrid = [[0,1],[0,0]]
Output: 1
Constraints:
m == obstacleGrid.lengthn == obstacleGrid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100obstacleGrid[i][j]is0or1.
My Solution
Compare the question T62 above, this question need to consider the following two things:
- During initialisation of the first line and the first column, we need to consider if there is an obstacle along the only path.
- During the path calculation, we need to consider if there are obstacles at the upper or left grid.
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
//Init the first line and the first column
int results[][] = new int[m][n];
boolean hasStone = false;
for (int i=0; i<m; i++){
if (obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0 && !hasStone){
results[i][0] = 1;
} else {
hasStone = true;
results[i][0] = 0;
}
}
hasStone = false;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++){
if (obstacleGrid[0][i] == 0 && !hasStone){
results[0][i] = 1;
} else{
hasStone = true;
results[0][i] = 0;
}
}
//Calc the path
for (int y=1;y<m; y++){
for (int x=1; x<n;x++){
if (obstacleGrid[y][x] == 1){
results[y][x] = 0;
} else {
results[y][x] =
(obstacleGrid[y-1][x] == 1 ? 0 : results[y-1][x]) +
(obstacleGrid[y][x-1] == 1 ? 0 : results[y][x-1]);
}
}
}
return results[m-1][n-1];
}
}
Dynamic programming in handling strings
T5. Longest Palindromic Substring
Given a string s, return the longest palindromic substring in s. (最长回文子串)
Example 1:
Input: s = "babad"
Output: "bab"
Explanation: "aba" is also a valid answer.
Example 2:
Input: s = "cbbd"
Output: "bb"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000sconsist of only digits and English letters.
My Solution
We can learn from the question that
- The substring with length 1 is always palindromic
- The substring with length 2 need to check if the two characters are the same
- The substring longer than 3 need to check
- The two edge characters are the same
- The substring without the edge characters is palindromic
Therefore, we can have the transformation function:
We can use a boolean table to represent whether the substring is palindromic or not.
For example, for "babad" we can learn:
| i \ j | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | T | F | T | F | F |
| 1 | T | F | T | F | |
| 2 | T | F | F | ||
| 3 | T | F | |||
| 4 | T |
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int len = s.length();
//Boundary situations
if (len <= 1){
return s;
}
//Init the results
boolean[][] results = new boolean[len][len];
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
for (int j=0; j<len; j++){
results[i][j] = (i==j);
}
}
//State transformation function:
//f(i,j) = (Si == Sj) && f(i+1, j-1)
//We need to iterate the length of the substring instead of the position of i and j
for (int L=2; L<=len; L++){
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
int j = i + L - 1;
if (j >= len){
//Out of boundary
break;
}
if (L > 2){
//Length is bigger than 2
results[i][j] = s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && results[i+1][j-1];
} else {
//Length is 2
results[i][j] = s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j);
}
}
}
//Find the longest from results
int maxLen=1;
int maxI=0;
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
for (int j=i+1; j<len; j++){
if (results[i][j] && (j-i+1) > maxLen){
maxLen = (j-i+1);
maxI = i;
}
}
}
return s.substring(maxI, maxI + maxLen);
}
}
T139. Word Break
Given a string s and a dictionary of strings wordDict, return true if s can be segmented into a space-separated sequence of one or more dictionary words.
Note that the same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.
Example 1:
Input: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet","code"]
Output: true
Explanation: Return true because "leetcode" can be segmented as "leet code".
Example 2:
Input: s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple","pen"]
Output: true
Explanation: Return true because "applepenapple" can be segmented as "apple pen apple".
Note that you are allowed to reuse a dictionary word.
Example 3:
Input: s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats","dog","sand","and","cat"]
Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 3001 <= wordDict.length <= 10001 <= wordDict[i].length <= 20sandwordDict[i]consist of only lowercase English letters.- All the strings of
wordDictare unique.
My Solution (timeout)
My solution should work but it cost too much time.
package T139;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class WordBreak {
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
int len = s.length();
List<Integer> wordLens = new ArrayList<>(len);
for (String word : wordDict){
wordLens.add(word.length());
}
Set<String> wordDictSet = new HashSet(wordDict);
//Edge situation
if (len == 1) {
for (String str : wordDict) {
if (s.equals(str)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//results[i][j] == true means the substring from i to j is in the dict
boolean[][] results = new boolean[len][len];
//Iterate by length of substring
int i, j;
String sub;
for (int L = 1; L <= len; L++) {
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
j = i + L - 1;
if (j >= len) {
break;
}
sub = s.substring(i, j + 1);
if (wordDictSet.contains(sub){
results[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
//Fetch result
return dfs(results, len, 0);
}
//DFS timeout
private boolean dfs(boolean[][] results, int len, int i) {
if (i == len) {
return true;
}
boolean found = false;
for (int j = i; j < len; j++) {
if (results[i][j] && !found) {
found = dfs(results, len, j+1);
}
}
return found;
}
}
Official Solution
We share the same idea that we need to use an array to store the previous results. I use a 2-dimension array to store from i to j but it shouldn't be that complicated. We can break down this problem into a smaller question:
- Can we break the substring from 0 to into two pieces, which the first piece 0 to can be break and the second piece to is a word in the dictionary. We start the from 1 because the empty string can always be broke.
In this way, the dp[j] represent that if the substring from 0 to can be broke, and we check the last word from to . Then, we iterate the to the length of the string s
public class Solution {
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
Set<String> wordDictSet = new HashSet(wordDict);
boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (dp[j] && wordDictSet.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
}